Understanding package manager and Systemctl
#90 Days of DevOps Challenge - Day 7
What is a package?
In the context of software development, a package refers to a collection of files and resources that are bundled together to perform a specific functionality or provide a set of related features. It is a way to organize and distribute software components, libraries, or modules in a structured manner.
Packages are commonly used in programming languages and operating systems to facilitate code organization, reuse, and distribution. They help manage dependencies, versioning, and installation of software components.
Different kinds of package managers.
In Linux, package managers play a crucial role in managing software installation, updates, and dependencies. Here are some of the popular package managers used in Linux distributions:
APT (Advanced Package Tool): APT is the package manager used in Debian-based distributions such as Debian, Ubuntu, and Linux Mint. It uses the .deb package format and provides a high-level interface for package management operations. APT is known for its powerful dependency resolution capabilities.
YUM (Yellowdog Updater, Modified): YUM is the package manager primarily used in Red Hat-based distributions such as CentOS and Fedora. It uses the .rpm package format and enables users to install, update, and remove packages with ease. YUM has been replaced by DNF in newer versions of Fedora.
DNF (Dandified YUM): DNF is the next-generation package manager, replacing YUM in recent Fedora releases. It retains the features of YUM but offers improved performance, better dependency handling, and an enhanced command-line interface.
Zypper: Zypper is the package manager used in openSUSE and SUSE Linux Enterprise distributions. It supports the .rpm package format and provides a robust set of features for package management, including dependency resolution and system updates.
Pacman: Pacman is the package manager used in Arch Linux and its derivatives, such as Manjaro. It follows a rolling release model and uses the .pkg.tar.xz package format. Pacman is known for its simplicity, speed, and comprehensive package management capabilities.
Portage: Portage is the package manager used in Gentoo Linux. It uses a source-based approach, where packages are built from source code based on user-defined configuration. Portage offers extensive customization options and dependency management.
These are just a few examples of package managers used in Linux distributions. Each package manager has its own set of commands and features, but they all serve the purpose of simplifying software management and ensuring system stability by handling dependencies and updates.
systemctl and systemd
Systemd is a system and service manager for Linux operating systems. It is designed to provide a centralized and standardized way of managing system services, processes, and resources. Systemd replaces the traditional init system and provides numerous features and benefits.
Systemctl is a command-line utility that interacts with
systemd. It allows administrators to control and manage system services and units. Here are some key aspects ofsystemctlandsystemd:Service Management:
Systemctlis used to start, stop, restart, enable, disable, and check the status of system services. It provides a simple and consistent interface for managing services across different Linux distributions.Unit Files: Systemd organizes system services and resources using unit files. These files define the configuration and behaviour of services, targets, sockets, timers, and other system entities. Unit files are typically stored in the
/etc/systemd/systemdirectory.
Install docker in your system from your terminal using package managers
Step 1:- Update your system packages by running the following command
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade -y # -y is the option to type "yes" while installing the services.Step 2:- Need to Install Docker
sudo apt-get install docker.io -yStep3:- To check the version need to run the below command
docker --version or docker -v
Step 4:- To check the Docker service status
systemctl status docker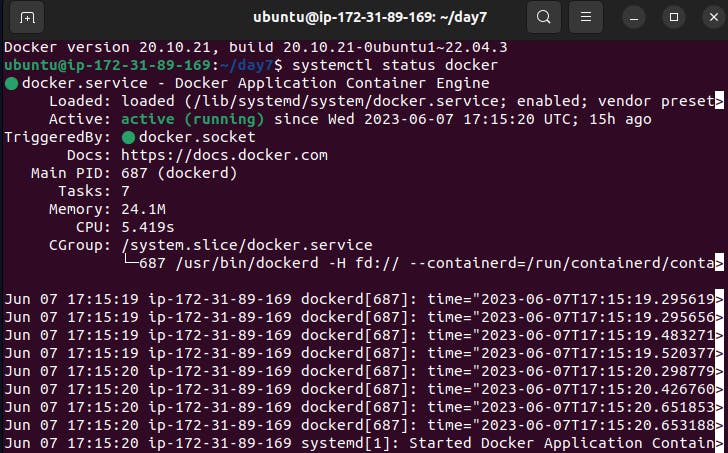
Step 5:- If the docker service has not yet started then need to run the below command to start the docker service
systemctl start dockerStep 6:- Verify that Docker is running correctly by running the below
sudo docker run hello-world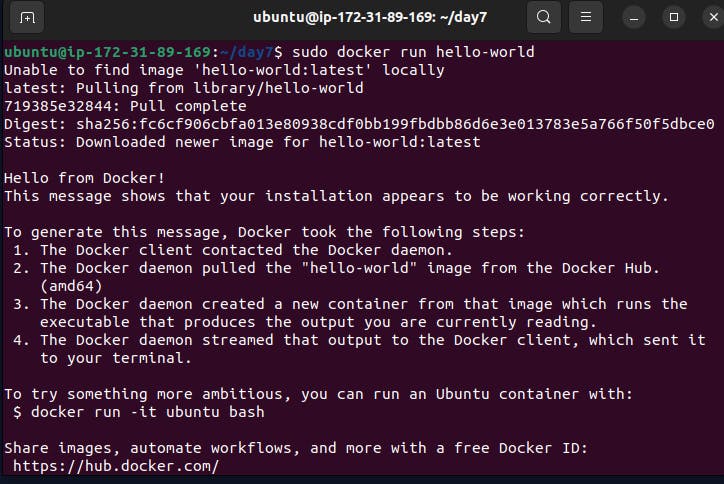
Install Jenkins in your system from your terminal using package managers
Step 1:- Update your system packages by running the following command
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade -y # -y is the option to type "yes" while # installing the services.Step 2:- Jenkins requires
Javato run, yet certain distributions don’t include this by default and some Java versions are incompatible withJenkins. so we need to install Java by following the commandsudo apt-get install openjdk-11-jdk -y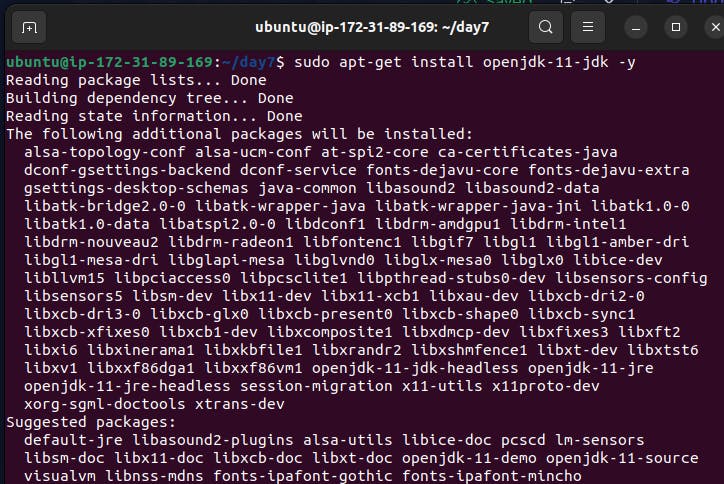
Step 3:- To check the
Javaversionjava --version
Step 4:- Now we can run the command to install the Jenkins with some installation keys below
curl -fsSL https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian/jenkins.io-2023.key | sudo tee \ /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc > /dev/null echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] \ https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian binary/ | sudo tee \ /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install jenkins -y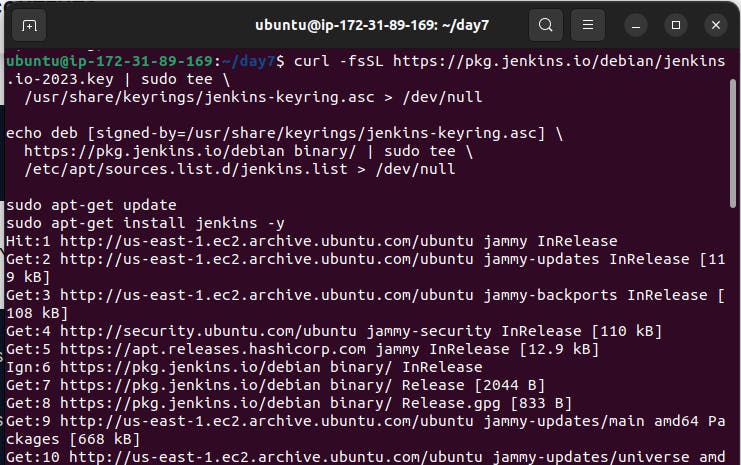
Step 5:- You can enable the Jenkins service to start by following the command.
sudo systemctl enable jenkins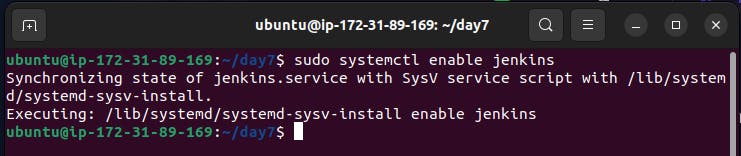
Step 6:- You can start and stop the Jenkins service with the command:
sudo systemctl start jenkins sudo systemctl stop jenkins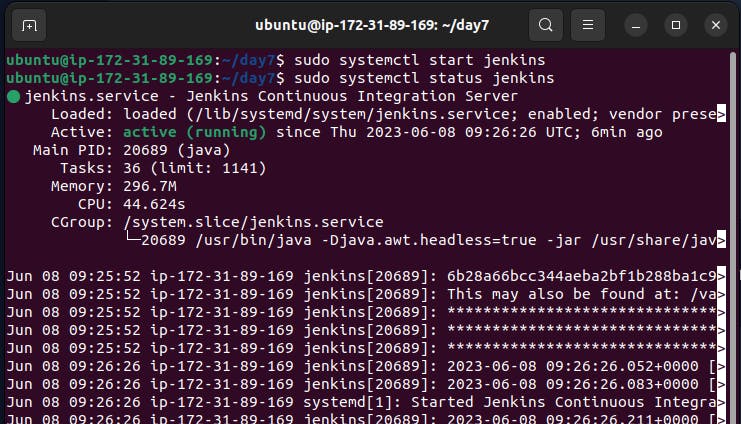
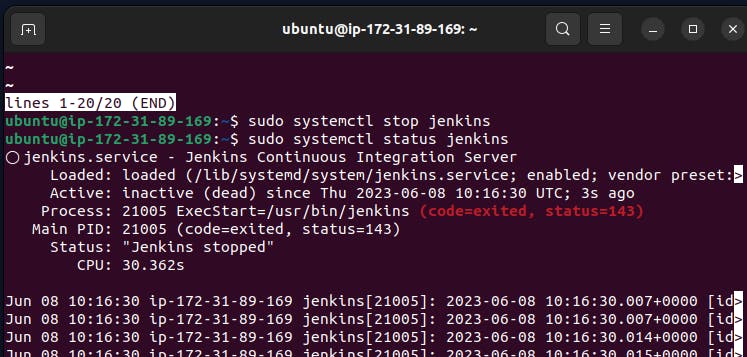
Stopping the Jenkins.
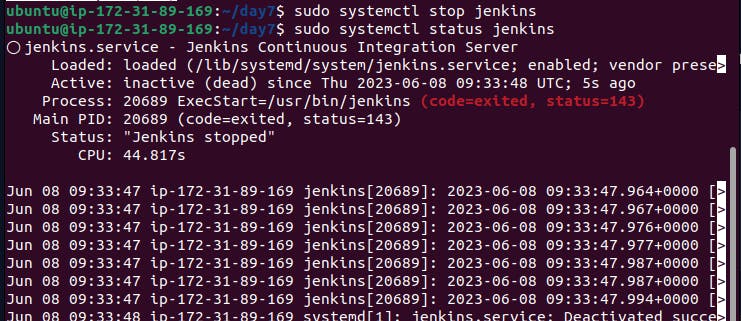
Step 7:- Check the status of the Jenkins service using the command:
sudo systemctl status jenkins

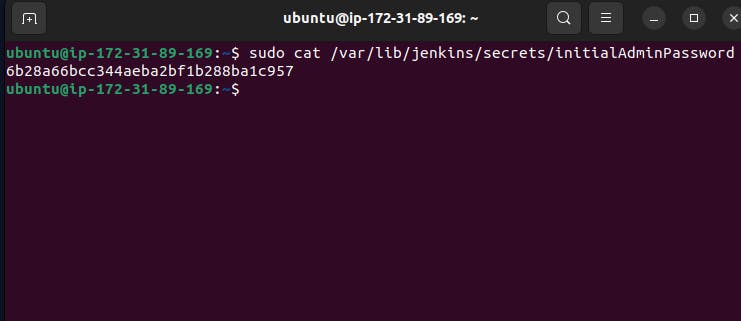
Step 8:- Now for accessing or landing on the Jenkins page we have to enable the PORT number in the security group of the server. Go to ec2 -> go to instance security group setting -> enable the port 8080 where Jenkins is running -> go to this " /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPasswordpath " copy the password and paste it to the place of a password.
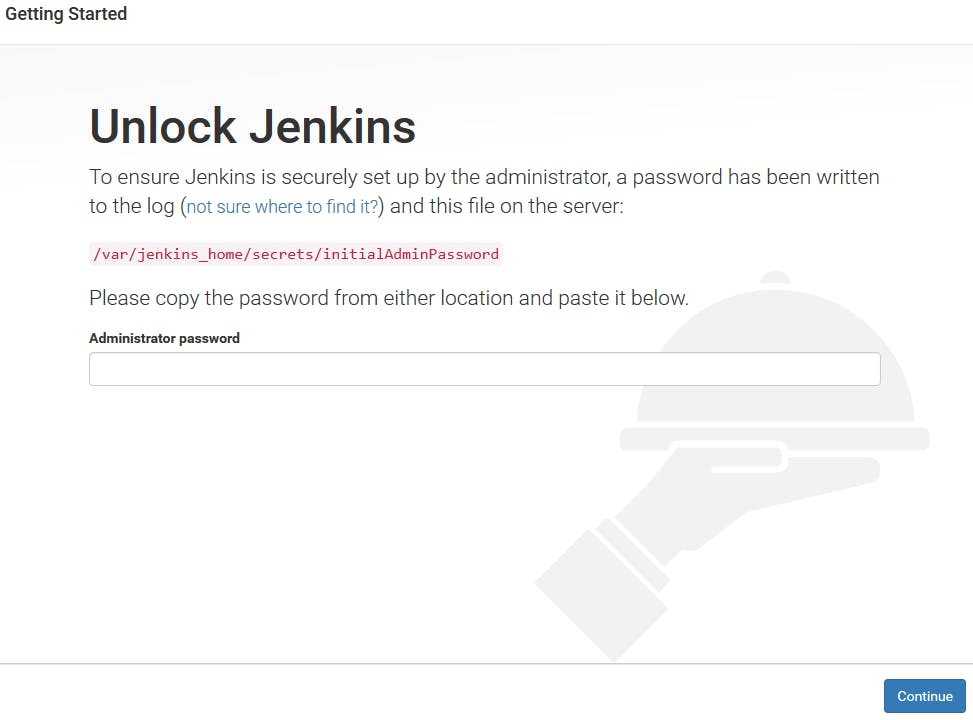
password is in this path so type this ,
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
After this Enter the password and u will redirect to Jenkins's home page.
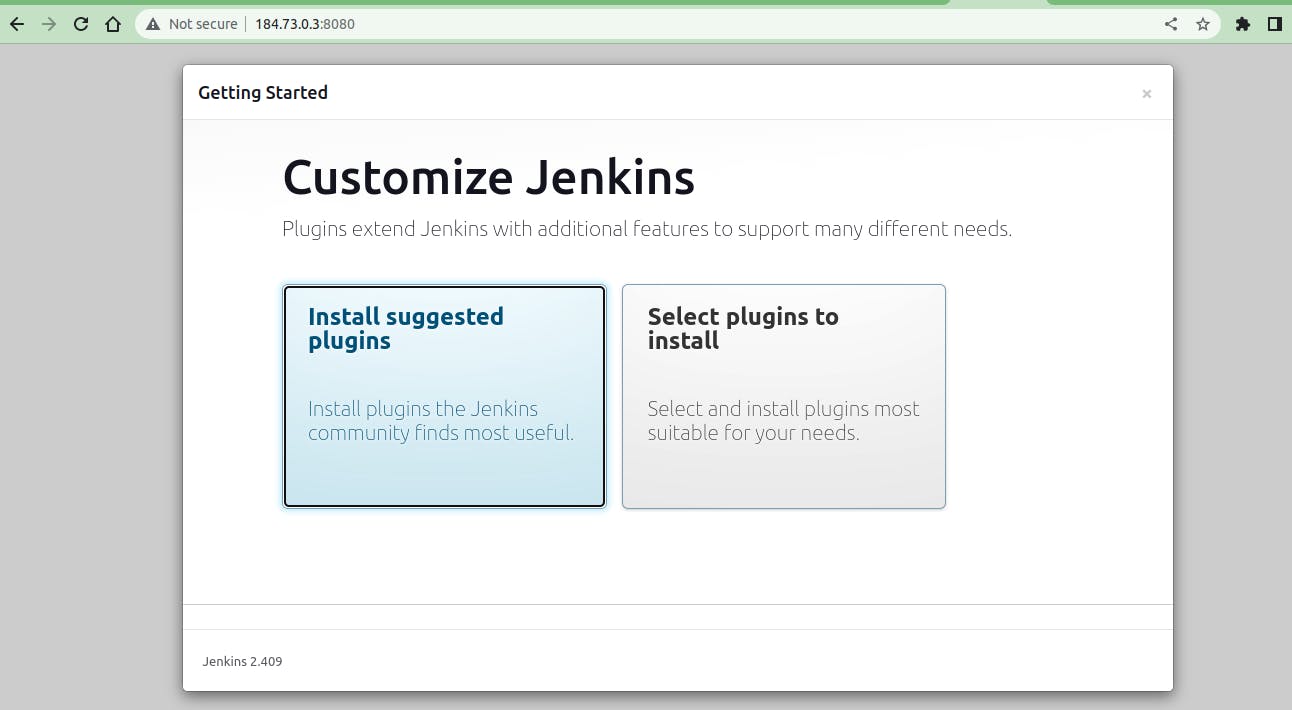
Now its time to complete the tasks
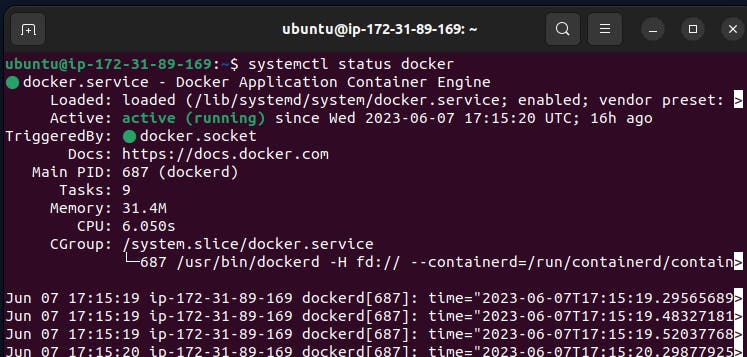
Check the status of the docker service in your system
systemctl status docker
Stop the service Jenkins and post before and after screenshots
Before:-
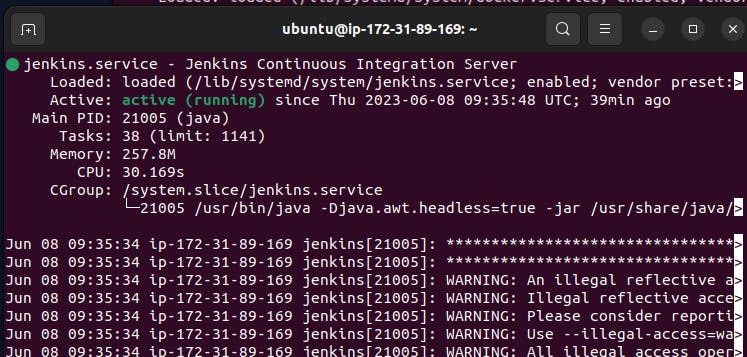
After :=
Read about the commands systemctl vs service
Systemctl and Service are both used for managing services in Linux, but they serve different purposes and have different functionalities.
- Service: The
servicecommand is a simple and legacy command used for managing services in Linux. It provides a convenient way to start, stop, restart, enable, disable, and check the status of services. It interacts with the init system (such as SysV init or Upstart) to manage services.
- Service: The
Example usage of the service command:
shellCopy codesudo service apache2 start
sudo service nginx stop
sudo service ssh restart
sudo service mysql status
- Systemctl: systemctl is a more powerful and modern command that is part of the system init system. It is used to control and manage services, units, and other aspects of the system. Systemd is the default init system in most modern Linux distributions.
Systemctl offers more advanced features and flexibility compared to the service command. It can handle dependencies, parallelize service startup, manage system targets, and provide detailed control over service behaviour.
Example usage of the systemctl command:
shellCopy codesudo systemctl start apache2
sudo systemctl stop nginx
sudo systemctl restart ssh
sudo systemctl status mysql
Thank you for taking the time to read this article on DevOps and #90daysofDevOps! I sincerely hope you found it helpful and informative.
If you have any questions or suggestions for improvements, please don't hesitate to reach out. Your feedback is valuable to me.
Wishing you continued success and happy learning on your DevOps journey!